ABSTRACT: 0532
Egf receptor inhibitor sc-120 disrupts Tgf-▀2 activity in sutures
| J. KAYNE1, J.T. RAWLINS2, C.R. FERNANDEZ1, and L.A. OPPERMAN1, 1Texas A&M Health Science Center, Baylor College of Dentistry, Dallas, USA, 2Ohio State University, Columbus, USA |
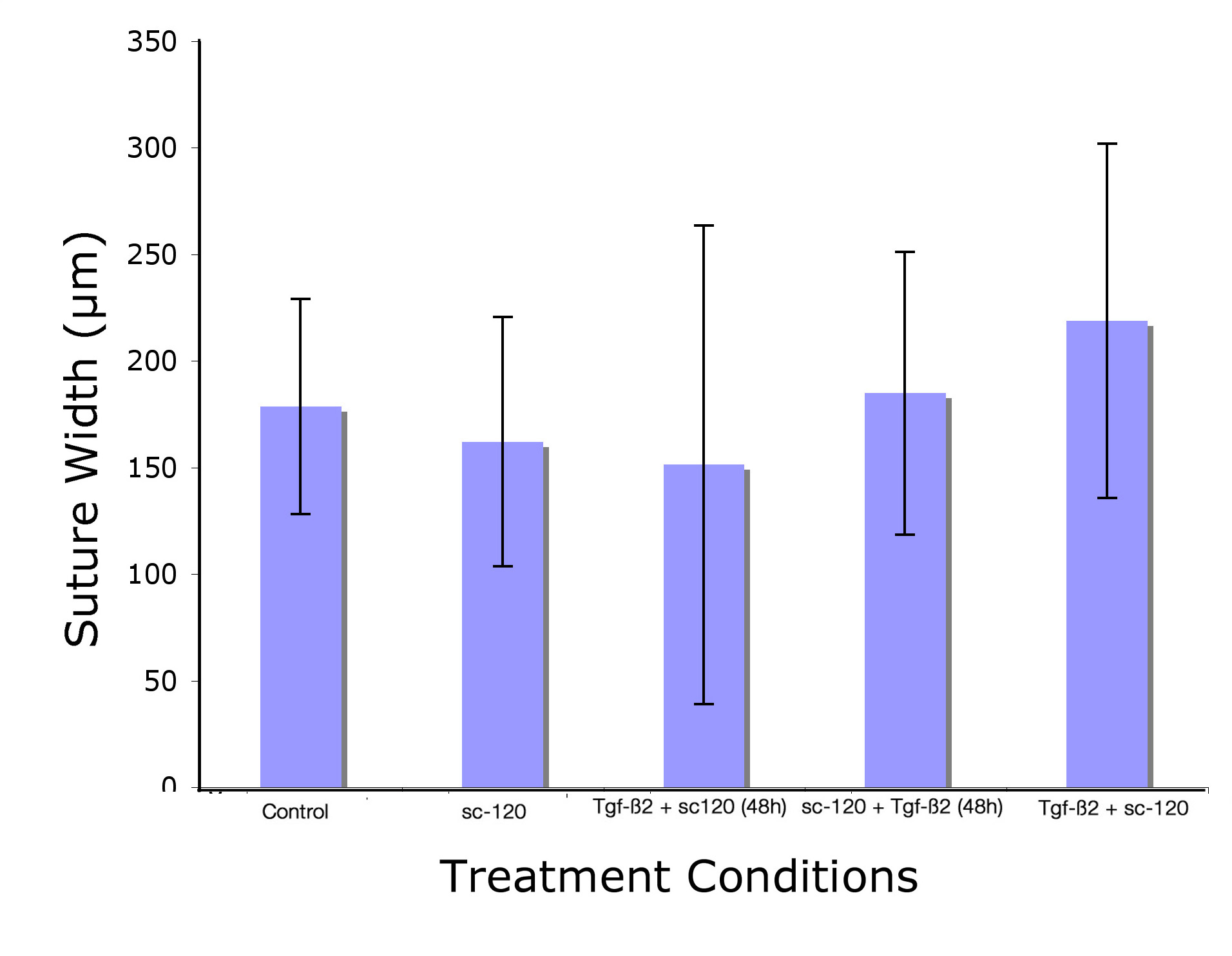
Objective: Tgf-▀2 induces Egf expression prior to induction of suture fusion. However, Egf alone does not induce suture closure. Pretreatment of calvariae with Egf blocks Tgf-▀2-induced suture closure, whereas post treatment has no effect on Tgf-▀2-induced suture closure. This study was done to test if Egf receptor signaling modulates Tgf-▀2 activity in sutures. Methods: Twenty E17.5 mice were sacrificed, their calveriae dissected and cultured for 5 days in 1) serum free medium (SFM) alone, 2) SFM plus 50mM sc-120 (sc-120), 3) SFM and 3 ng/ml Tgf-▀2 (Tgf-▀2), with sc-120 added at 48 hours, 4) SFM and sc-120, with Tgf-▀2 added at 48 hours, and 5) SFM with sc-120 and Tgf-▀2 with n=4 per group. Tissues were then harvested and prepared for histological sectioning of coronal sutures and H&E staining. Sutures were viewed under a microscope and the shortest distances between bone fronts across the suture were measured using Metamorph«. Data was stored in an Excel file and averages and standard deviations calculated within each group and between the groups. Results: No significant differences in suture width were found within or between the groups, demonstrating that blocking Egf receptor activity either before or after Tgf-▀2 treatment blocked Tgf-▀2-induced suture closure. Conclusion: Since Egf alone does not induce suture closure, it was not unexpected that sc-120 alone had no effect on suture width. That blocking Egf activity after Tgf-▀2 treatment abrogates suture obliteration indicates Tgf-▀2 requires Egf signaling to induce suture closure. An unexpected finding was that blocking Egf receptor activity prior to Tgf-▀2 treatment also blocked Tgf-▀2 induced suture closure. However, since sc-120 was present for the duration of culture, it is likely that the presence of sc-120 after Tgf-▀2 treatment was responsible for blocking the Tgf-▀2 effect on sutures. |
| Seq #83 - Craniofacial Developmental Biology and Genetics 8:00 AM-9:30 AM, Friday, April 4, 2008 Hilton Anatole Hotel Grand Ballroom A |
©Copyright 2008 American Association for Dental Research. All Rights Reserved.