ABSTRACT: 1266
Fluoride Recharge of a New Protective Coating
| J.A. FITCH1, J.E. SWANSON1, K.M. CUMMINGS1, A.M. PFARRER2, and R.P. RUSIN1, 13M ESPE Dental Products, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2OMNI Preventive Care, A 3M ESPE Company, West Palm Beach, FL, USA |
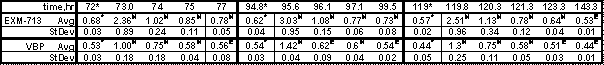
Objectives: Compare the fluoride recharge of an experimental coating material, EXM-713, to another RMGI material, 3M™ ESPE™ Vitrebond Plus Liner/Base. EXM-713 is a resin-modified glass ionomer coating material. Methods: Cured 20x1mm disks were stored separately in deionized water at 37°C. Fluoride release was measured after 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 24, 48, and 72hr using fluoride selective electrode and TISAB II. Dentifrice treatments were applied at 72, 95, and 119hr; fluoride data were collected at 1, 2, 3, 5, 24hr after each treatment; treatment comprised soaking disk 2min in slurry of 3M™ ESPE™ ControlRx™ 5000ppm Fluoride Prescription Dentifrice with deionized water (water:dentifrice=3:1). Data after treatment were compared to immediately before treatment via one-way paired T-test (p<0.05). Results: Cumulative fluoride release rate, microgramF/cm2/hr (n=5). Within each recharge period and material, groups with superscript * are pre-recharge, H are higher than pre-recharge, E are equivalent to pre-recharge (p>0.05).
Conclusions: The fluoride release rate of both EXM-713 and VBP is higher after dentifrice treatment versus before, lasting up to 5 hr for EXM-713, 3hr for VBP. The recharge levels at 95 hr and 119 hr were not statistically different, but statistically higher than at 72 hr, showing that the effect is repeatable. EXM-713 and VBP can repeatably recharge and re-release fluoride from application of a prescription-strength dentifrice. |
| Seq #179 - Late Breaking News 10:45 AM-12:00 PM, Saturday, April 5, 2008 Hilton Anatole Hotel Trinity I - Exhibit Hall |
©Copyright 2008 American Association for Dental Research. All Rights Reserved.