ABSTRACT: 0630
Effect of Galla chinensis on remineralization of bovine root carious
| B. GUO, K. QUE, X. ZHOU, J. YANG, J. LIU, Q. XIA, and F. YANG, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China | |
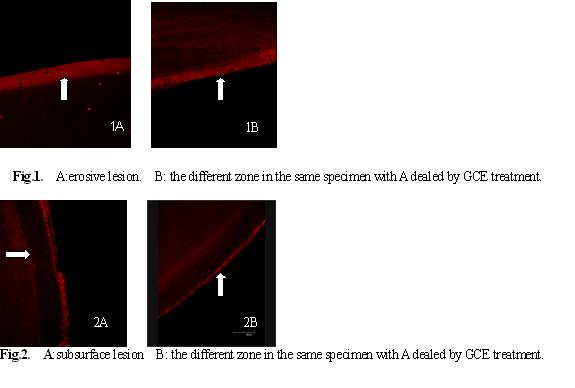
Objectives: Root caries has been considered as one of the most popular oral diseases in the elders. Some papers have been demonstrated that Galla chinensis can inhibit enamel demineralization and enhance enamel remineralization, but less paper was studied for root carious lesions systematically. The study was aimed to evaluate the effect of effective compounds of Galla chinensis on the remineralization of different root carious morphous in vitro. Methods: Sixty bovine dentine blocks were divided into two teams and demineralized individually by two levels of demineralization solutions(to form erosive lesion and subsurface lesion ) in vitro. Ten specimens of every team were handled by one of three treatments: remineralization solution(positive control); deionized water (negative control); 4000 ppm aqueous solutions of G. chinensis extract (GCE). The dentine blocks were subjected to a pH-cycling regime for 7 days. Each daily cycle included 21 hrs deal and 3 hrs demineralization applications within the fore 4 days. The latter 3 days dentine blocks were deal the whole day. Two specimens of each team were taken out and watched by polarized light microscope. Data observed by Laser scanning confocal microscope(LSCM) were computerized and analysed. Results: the remineralization ability of GCE on both artificial carious lesion patterns were apparent and enhance the remineralization of the specimens(Fig 1,2 P<0.05). The remineralization lever of GCE for the erosion lesion was lower than that for subsurface lesion (AF , -10.2800±1.71197 vs -21.7688±3.001 98P<0.05). Under subsurface lesion, The remineralization lever of GCE was higher than that of remineralization solution(-21.7688±3.04198 vs-7.2163±2.39719, P<0.05). There was no significant difference for erosive lesion remineralized by GCE and remineralization solution (-10.2800±1.71197 vs -6.2038±1.30794, P>0.05). Conclusions: The present study has demonstrated the potential of GCE to improve remineralization of artificial carious lesions under dynamic pH-cyclic conditions. This findings support the proposition that Galla Chinesis may be a promising anti-caries natural medicine in the future.
| |
| Seq #86 - Fluoride/Caries Inhibition 2:00 PM-3:15 PM, Thursday, July 3, 2008 Metro Toronto Convention Centre Exhibit Hall D-E | |
©Copyright 2008 American Association for Dental Research. All Rights Reserved.