ABSTRACT: 1793
Pre-heating influence on the conversion degree of composite luting materials
| P.A. ACQUAVIVA1, M. GAGLIANI2, F. MANGANI3, G. ADAMI1, F. CERUTTI1, and A. CERUTTI1, 1University of Brescia, Italy, 2University of Milan, Italy, 3University of Rome - Tor Vergata, Roma, Italy | |
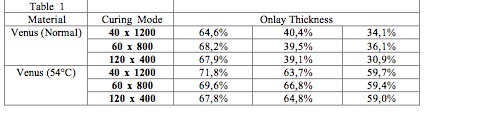
Objectives: Physical and chemical properties of luting agents are strictly related to polymer conversion degree. This study evaluated how pre-heating influences the composite luting materials conversion. Methods: Onlays of different and defined thickness (2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm) were made in Signum (Heraeus) composite material, shade A3.5, and they were cemented onto a glass plate with the same composite luting agent (Venus, Heraeus) employed in two different temperatures (room temperature and, after pre-heating in an apposite oven, 50°C). Light-curing was performed with three different modalities (1200 mW/cm2 for 40 s, 800 mW/cm2 for 60 s, and 400 mW/cm2 for 120 s) with the same halogen lamp (Swiss Master Light, EMS), using a shielded-all-around tip to induce light reach the cement only through the onlay. Eighteen onlays were divided into 6 groups (n=3). Each sample was examined in three points (centre, middle, margin) by Micro-Raman spectrometer (DILOR HR Labram) to evaluate the polymer conversion degree. All results were analysed by ANOVA test (p<0,001). Results: The pre-heated composite material reaches high degrees of conversion in all the tested combinations, while the room temperature composite has no satisfactory results in case of thick restorations. Conclusions: Restoration thickness influences the conversion rate of the luting agent. Preheated material increases significantly the conversion rates.
| |
| Seq #187 - Polymerization Processes 2:00 PM-3:15 PM, Friday, July 4, 2008 Metro Toronto Convention Centre Exhibit Hall D-E | |
|
Back to the Dental Materials 5: Polymer-based Materials - Chemistry and Composition Program | |
©Copyright 2008 American Association for Dental Research. All Rights Reserved.