ABSTRACT: 1479
Interfaces between glass ionomers and normal and caries affected dentin
| L.M. PINZON1, R. STANISLAWSKI1, L.G. WATANABE1, S.A. GANSKY1, J.A. WEINTRAUB1, A. TOMSIA2, S.J. MARSHALL1, and G.W. MARSHALL1, 1University of California, San Francisco, USA, 2Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, CA, USA | |
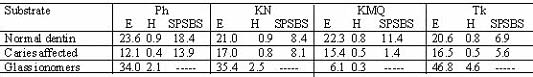
Objectives: To determine the bond strength (BS), nanomechanical properties [hardness (H) and elastic modulus (E)] and interfacial morphology of four glass ionomers bonded to sound and caries affected dentin. Methods: One of four glass ionomers: Ketac Molar Quick (KMQ, 3M-ESPE), Ketac Nano (KN, 3M-ESPE), Photoc (Ph, GC-America), Tokuso (Tk, Tokuyama) was applied to each of 12 permanent sound human teeth (dentin ground to 320-grit) and 12 caries affected human teeth (caries removed manually using a spoon excavator). Specimens were stored in HBSS at 37°C for 24h. Cross sections of the bonded interfaces (n=3/group) were polished to 0.25 µm. Lines of ~30 nanoindentations were made at 1µm intervals across the dentin/glass ionomer interface. Single Plane Shear Bond Strength (SPSBS) was measured (n=7/group) at a cross-head speed of 5 mm/min. Failure modes for bond strength specimens were determined at 100X. Specimens were treated with 5N HCl/5% NaOCl or fractured perpendicular to the interface and gold sputter-coated to reveal any hybrid layer. Results: H, E and SPSBS were analyzed using 2-way mixed effects ANOVA (H&E) and ANOVA (SPSBS) There were significant differences among GIs by dentin substrate (GIxSubstrate p<0.0001) in E and H. SEM showed interfacial microstructure morphologic differences among glass ionomers. No hybrid layers were found. Conclusions: Sound dentin restored with the different glass ionomers showed nanomechanical properties higher than caries affected dentin. Bond strengths were higher to sound dentin than caries affected dentin. Supported by NIH T32 DE07306; materials provided by GC-America 3M-ESPE, and Tokuyama.
| |
| Seq #142 - Interface 9:00 AM-10:30 AM, Friday, July 4, 2008 Metro Toronto Convention Centre Room 801B | |
|
Back to the Dental Materials 1: Adhesion - Bond Strength Testing and Mechanisms Program | |
©Copyright 2008 American Association for Dental Research. All Rights Reserved.