ABSTRACT: 3189
Effects of Filler Surface Treatment of Magnetic Composite Resin
| H. SOMA, and Y. MIYAGAWA, The Nippon Dental University School of Life Dentistry at Niigata, Japan | |
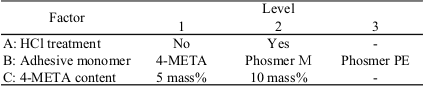
Objectives: A previous study showed that the treatment of filler by an adhesive monomer is necessary for a magnetic composite resin. However, the best kind of adhesive monomer and its applying method have not been examined. The purpose of this study was to find the effects of filler treatment condition in developing a magnetic composite resin for the keeper of magnetic attachment. Methods: SUS447J1 stainless steel (30% Cr, 2% Mo) particles (<0.02mm) were used as filler. The table shows the experimental factors and levels studied. A base resin containing BPO was prepared by dissolving 5% or 10% of 4-META in UDMA/MAA monomer. UDMA monomer containing DMPT was used as a catalyst resin. The base and catalyst resins were then mixed with the six kinds of treated filler particles to produce base and catalyst pastes. The filler content in each paste was 90%. After mixing of the two pastes, the flexural properties of twelve kinds of composites were measured at three replications according to the method described in ISO 4049:2000. The results were analyzed by three-way ANOVA.
Results: The flexural strength ranged from 40.9 MPa (A1B3C2) to 90.2 MPa (A1B1C1). The flexural strength was significantly affected by factor A, factor B, and their interaction (p<0.001). The elastic modulus ranged from 8.5 GPa (A2B3C2) to 19.6 GPa (A1B1C1), and was significantly affected by factor B (p<0.001), factor A (p<0.05), and factor C (p<0.05). Among the adhesive monomers, 4-META gave the highest strength and modulus, followed by phosmer M. The HCl treatment of filler rather decreased the strength and modulus. As for the 4-META content in base resin, 5% generally produced higher values than 10%. Conclusions: The filler surface treatment useful to develop a better magnetic composite resin has been clarified. | |
| Seq #296 - Prosthodontic and Maxillofacial Materials 1:45 PM-3:00 PM, Saturday, July 5, 2008 Metro Toronto Convention Centre Exhibit Hall D-E | |
©Copyright 2008 American Association for Dental Research. All Rights Reserved.